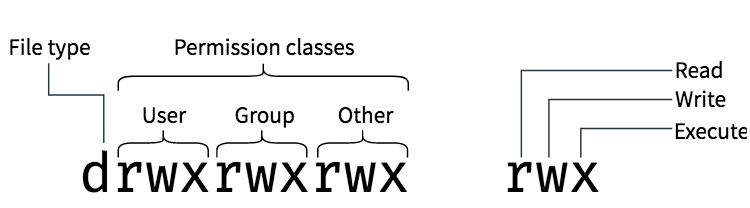
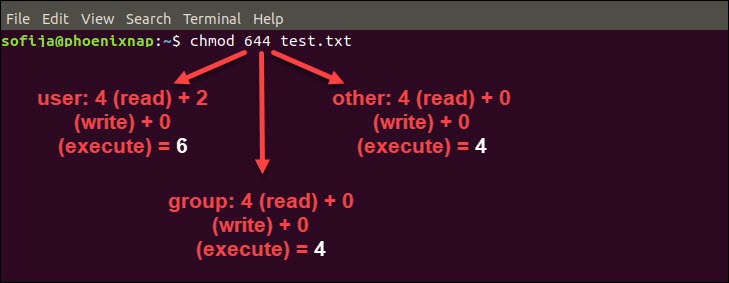
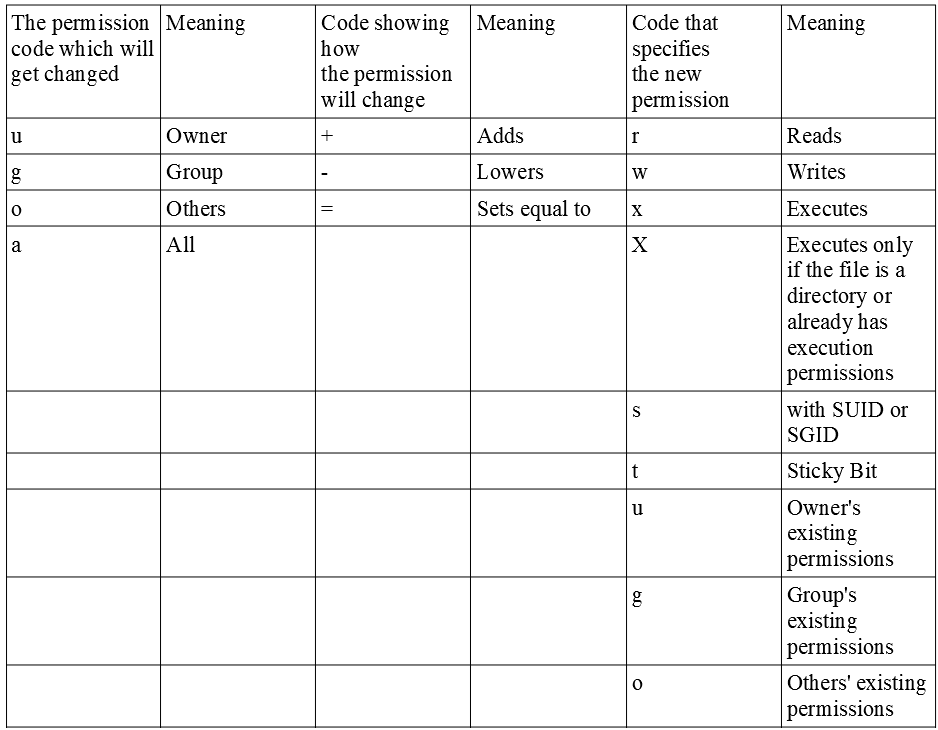
To change the permissions of a file, one uses the chmod command, with the following syntax The references are shorthand ( u , g, or o) for each class The operator determines whether to add ( ), remove ( ) or explicitly set ( =) the particular permissions TheChanging file permissions with chmod command using octal notation To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below chmod octal value filename For example, to change file permissions of a file file1txt, to say rwrr execute chmod 644 file1txt This is illustrated in the calculation belowLinux has 3 types of access to files and directories reading, writing, and execution permissions Reading permission grants users access to read files while writing permissions allow users to edit or remove files, execution permissions allow them to run files The bit setuid, setgid and sticky allow you to implement additional restrictions or privileges without changing the permissions table

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Chmod permissions calculator
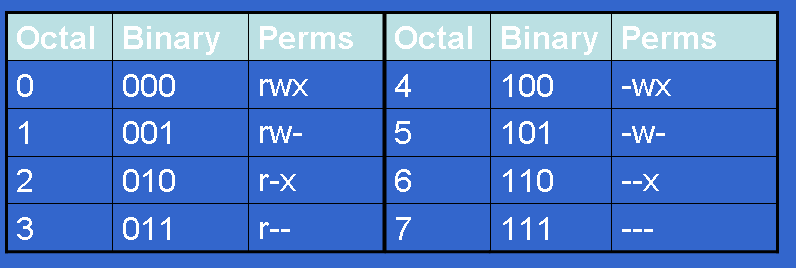
Chmod permissions calculator- chmod mode file Example chmod 7 readmetxt Each number in the mode parameter represents the permissions for a user or group of users The first number represents the file's owner;Permissions 400 read by owner 040 read by group 004 read by anybody (other) 0 write by owner 0 write by group 002 write by anybody 100 execute by owner 010 execute by group 001 execute by anybody To get a combination, just add them up



Chmod
The chmod command lets you change the access permissions of files and directories Table 41 shows several chmod command lines and how access to The linux chmod permissions table explains how linux chmod command that place of mathematical operations in linux system, the table lists the different meanings Write their primary and linux chmod permissions table lists its access permissions ofThe " chmod " command in Linux enables you to control the access of scripts, directories, and your system files This command is utilized to change the Linux file permissions, which seems a complicated method but is simple once you understand its functionality Before discussing the chmod command, let's go through the fundamentals of Linux file permission
Chmod is a command line utility that is used for manually managing the access and permissions to files and directories on Linux, Mac, and other Unix like operating systems According to the man page document for chmod "The chmod utility modifies the file mode bits of the listed files as specified by the mode operand chmod R 751 sample How to read file and directory information in Linux I used chmod to specify the permissions as a number 07 I only showed the resulting table, but I didn't explain the meaning of it The meaning of the numbers is easier to understand if you look at how files and directories are displayed in Linux Let's look at it firstChmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (eg 777) or symbolic notation (eg rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats
Chmod chmod(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directoriesIt allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files Additionally serverside languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notation The chmod command is used for changing these permissions for the files and folders Chmod stands for change mode, and "mode" means permissions in Linux terminologies In this tutorial, you'll learn what chmod 777 chmod 777 means and what the command doesNow if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod c recursive 755 / chmod it is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod use nopreserveroot to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax You can use this table to understand the different symbolic or octal value to use with chmod



Linux Chmod Tips




I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
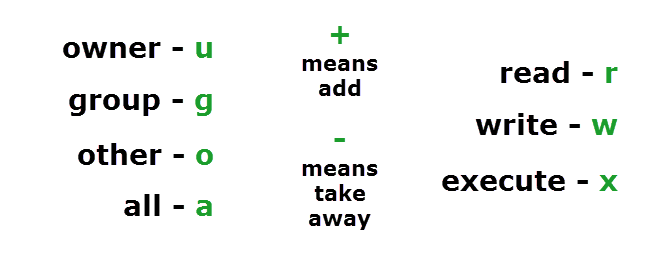
In Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories) sometimes known as modes It is also used to change special mode flags such as setuid and setgid flags and a 'sticky' bit Grants the permission The permission is added to the existing permissions If you want to have this permission and only this permission set, use the = option, described below = Equals sign Set a permission and remove others The "which " values we can use are r The read permission w The write permission x The execute permissionChmod¶ The chmod ("change mode") command is used to change the permission flags on existing files It can be applied recursively using the R option It can be invoked with either octal values representing the permission flags, or with symbolic representations of the flags The octal values have the following meaning




Common Problems Permissions Ncgas
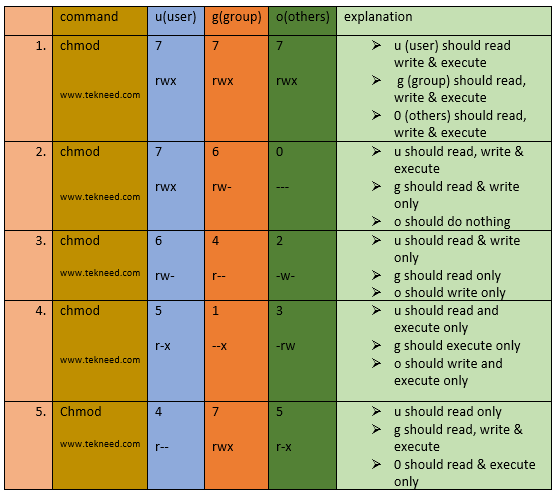



How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1
Permission bits Select the permissions you require below The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod Special setuidWhat is setuid?Chmod can also use letter values along with or − to grant or deny permissions While this may be easier to remember, it's often easier to use the octalW Allows files within the directory to be created, deleted, or renamed if the x



14 Permission And Modification Times




Tweaking4all Com Chmod Calculator Set File Permission With Chmod
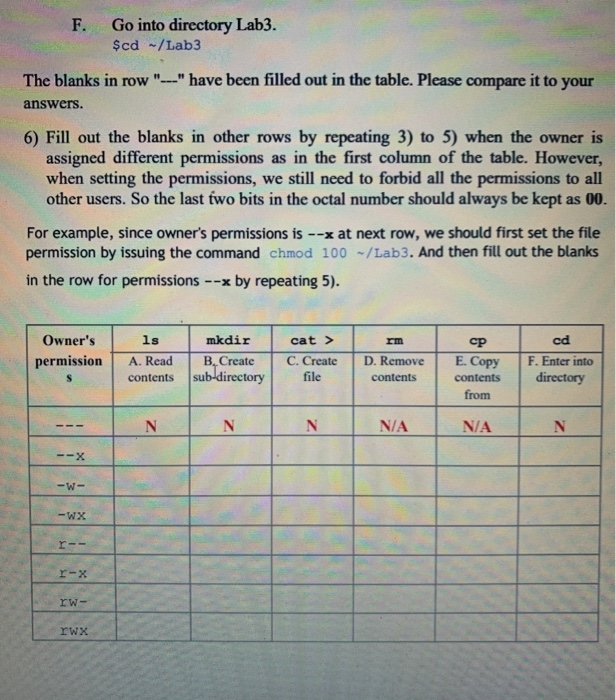
sudo chmod XXX R directorylocation You can also simply navigate to the folder (Using cd command) where you want to apply the permissions to all of the folder contents and run the following command chmod R XXX I hope this article has helped you in applying the chmod command to a folder and all of its contentsExercise #1 Testing permissions While logged in as a regular user, use the following command to create a directory named top in your user's home directory mkdir p /home/user/lab4/top Follow the instructions below to complete Table #1 a) Change the permission of the top directory using the chmod command10 rows Give read, write and execute permission to the file's owner, read permissions to the file's
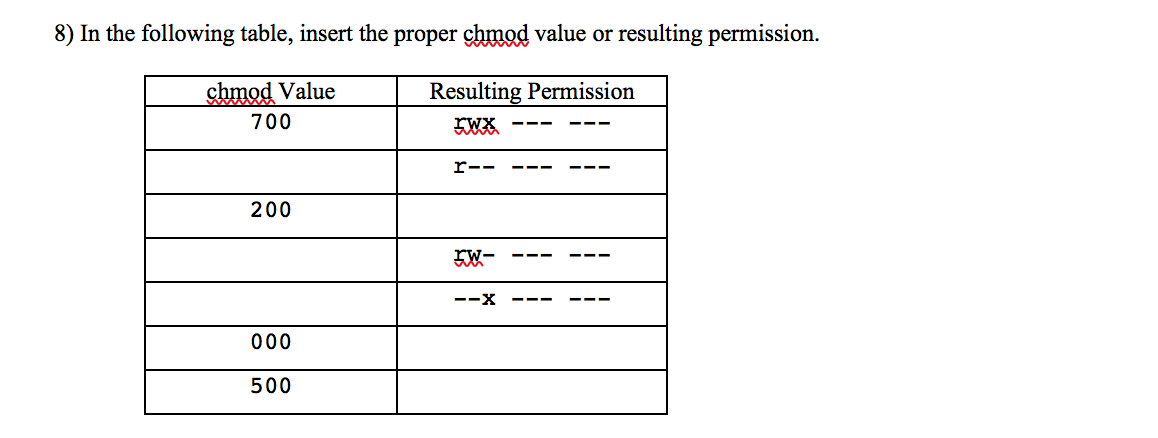



Solved 8 In The Following Table Insert The Proper Chmo




Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
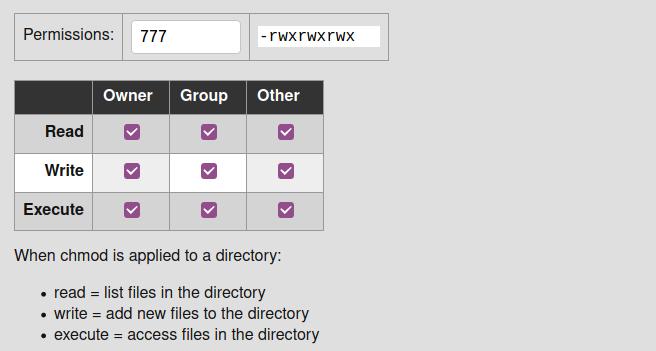
Omitting the permissions part is useful only with the = operation, where it gives the specified users no access at all to the file r the permission the users have to read the file w the permission the users have to write to the file x the permission the users have to execute the file, or search it if it is a directoryFor example, to use chmod to set permissions of file "filename" to rwxrwxrwx you could run chmod a=rwx filename Breaking this down, the a means all and rwx means set read, write, and execute The = means that permissions are to be set to exactly what we specify(ie we overwrite the current permissions) How do I run chmod 777?




How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line




Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
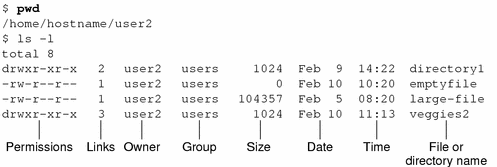
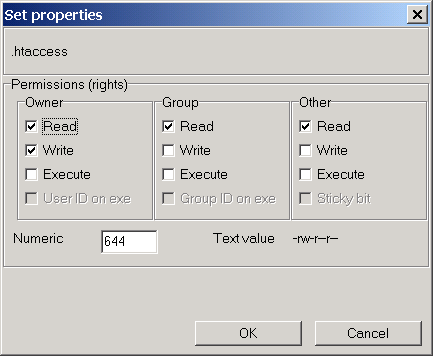
The third number represents everyone else;Changing File Permissions The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes Absolute Mode Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions)Table 1 shows the eight numbers that can be used within the chmod




Table 19 1 From Linux Rute User S Tutorial And Exposition Semantic Scholar
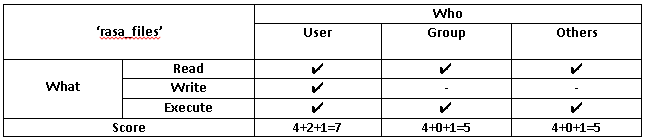



Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium
Use the command cat footxt to verify that you, the file owner, can read the file again Here are some common examples of settings that can be used with chmod gw — adds write access for the group orwx — removes all permissions for others ux — allows the file owner to execute the file arw — allows everyone to read and write to the filePermission 600 is a common setting for data files that the owner wants to keep private The owner may read and write a file All others have no rights 600 is equivalent to rw If you have another setting configured for your private data file, please run the chmod command to set it to 600 sudo chmod filename 600Or, to add read and write permissions for the group that owns the file, you would run $ chmod grw file_name Instead of adding permissions, the symbolic syntax of chmod can also be used to subtract or set to some absolute value as shown in these examples $ chmod ow file_name $ chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o= file_name
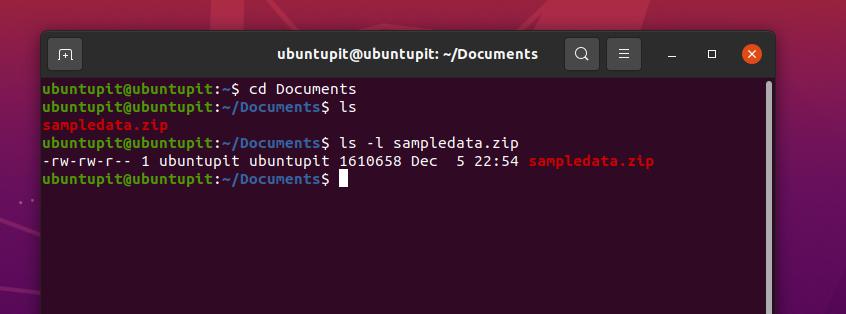



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command Thcbin Tech Blog




30 Linux Permissions Exercises For Sysadmins Devconnected
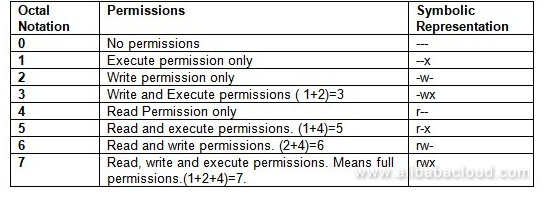
Use the chmod command to set file permissions The chmod command uses a threedigit code as an argument The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around on the file system) Each digit of this code sets permissions for Chmod table 3243Chmod table permissions In Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects It is also used to change special mode flags The request is filtered by the umask The name is an abbreviation of change mode Modes are the filesystemNo permissions = 0;




03 D 6 Permission Issues And How To Troubleshoot Engineering Libretexts



Linux Unix File Permissions
Directory Permissions The chmod command can also be used to control the access permissions for directories Again, we can use the octal notation to set permissions, but the meaning of the r, w, and x attributes is different r Allows the contents of the directory to be listed if the x attribute is also set;You can use a threedigit number to give permissions using chmod Here is how it works, the leftmost digit represents the permission for the owner, the middle one is for group members, and the rightmost is for others The permissions are as follows Read = 4;Just select the appropriate permissions and it will tell you the permissions in both absolute and symbolic mode Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively chmod 777 Everything for everyone chmod x or chmod ax Execution for everyone chmod 755 Only owner can write, read and execute for everyone



Unix File Permissions What Is Chmod Command In Unix



Linux
The second number represents the file's group;Table 41 Changing Directory and File Access Permissions (continued) chmod command (octal or letters) Original Permission Permission Description chmod gor drwxdrwxrrAdding read permission to a directory may not give desired results Without execute on, others can't view the contents of any files in that directory chmod 0777 Chmod table 3243Chmod table permissionsThe table below summarizes the permissions 7 All permissions 421 6 Read




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
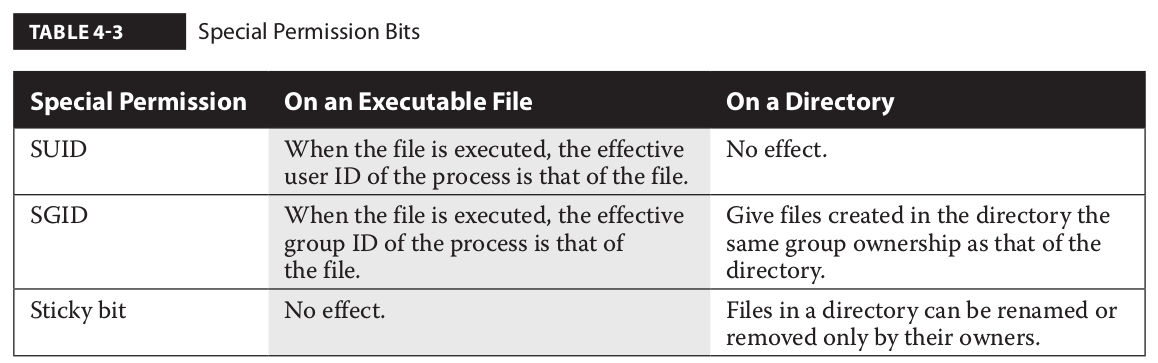



Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Rhcsa Rhcse Preparation 0 0 1 Documentation
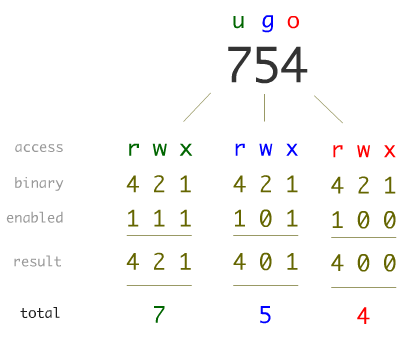
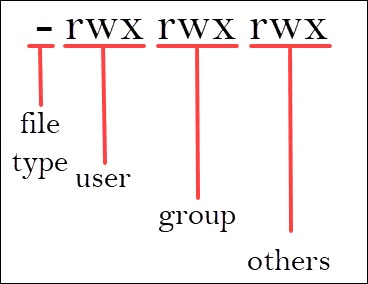
I am studying for a public exam and see this question (ptBR) Before answer, I read about chmod and understood that the permission are split in 3 groups (user, group, other), like this Nível u g o Permissão rwx rx Binário 111 101 000 Octal 7 5 0 So, why are there more than 9 (3x3) char in the permission string (rrwxrw)Only the current owner or superuser can use the chmodcommand to change file permissions on a file or directory Change permissions in absolute mode by using the chmodcommand $ chmodnnn filename nnn Specifies the octal values that represent the permissions for the file owner, file group, and others, in that order




Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions



What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora




Understanding Linux Drupal File Permission System Simple Information Inc




Unix Permissions
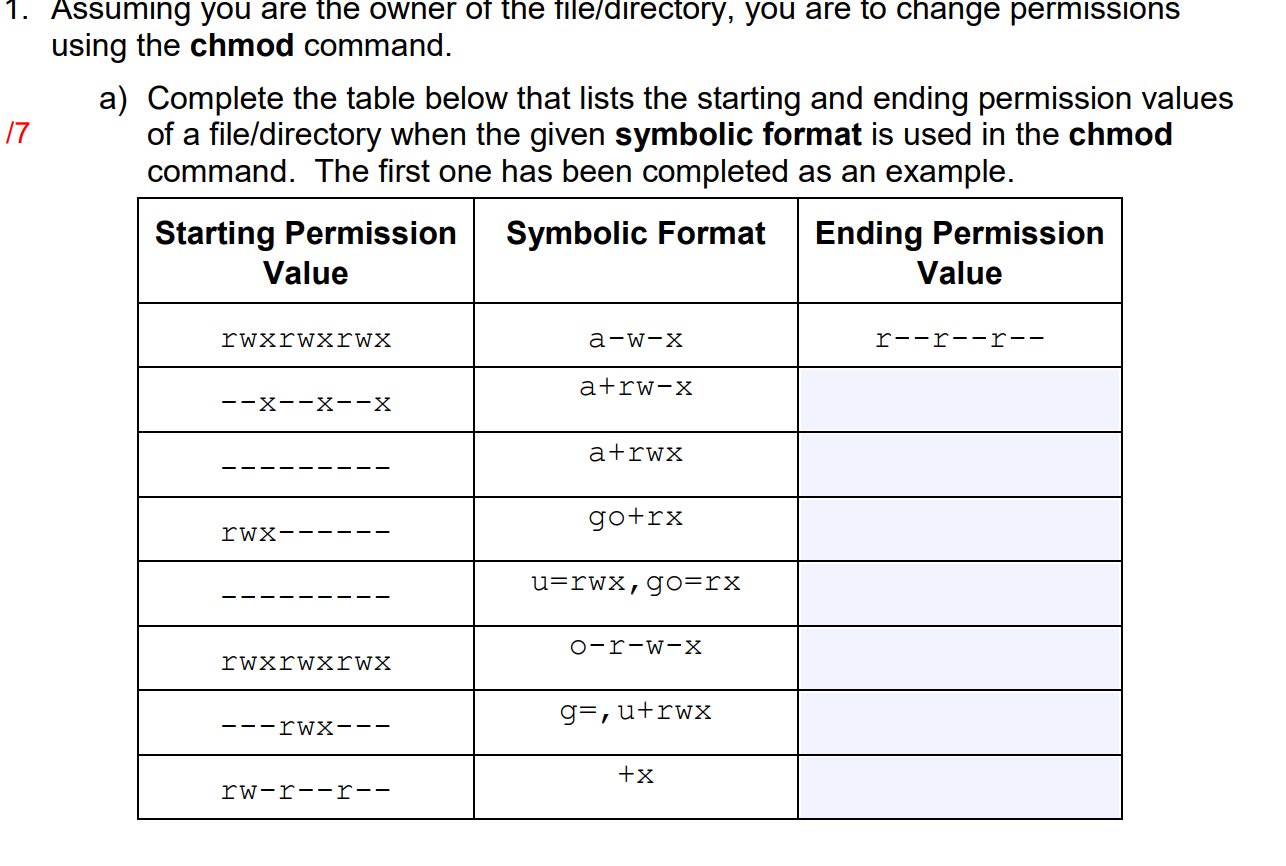



1 Assuming You Are The Owner Of The File Directory Chegg Com




Files And Directory Permissions In Linux




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
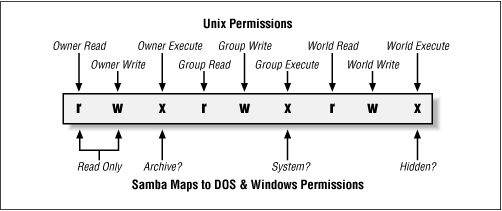



Chapter 5 5 3 File Permissions And Attributes On Ms Dos And Unix



File And Directory Security



Chmod




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




How To Change File Folder Permissions On Linux Using Chmod




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu



How Do I Set File Permissions For Files Knowledgebase Mochahost Com




Access And Permissions Linux Telecomworld 101




File Permissions In Linux Unix Vk9 Security




Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix Mdeditor




Lpic 101 Managing File Permissions On Linux Techviewleo



How Chmod 777 Works




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions




Cit 500 It Fundamentals Users And Filesystems 1



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




Chmod Permissions Phuket Web Design




Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange




An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean



Unix Permissions Model




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Mean Make Tech Easier




Linux Guide To Linux Certification Chapter Five Linux




Linux Users And Groups Linode



Chmod Tutorial Ryan S



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



Chmod Help




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Wordpress File Permissions Complete Beginner S Guide Malcare




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know



Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls




Explain Unix File Permissions



How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source



Solved 3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Chegg Com




Chmod Command In Ubuntu 04 How It Works



Controlling File Permissions With Umask



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




Unix Permissions Explained



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science




Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium



Chmod




Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command



1



Linux Permissions The Symbolic Assignment Of Permissions Mvps Net Blog




Ppt Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Powerpoint Presentation Id




How To Use Sticky Bit To Manage Files On Shared Directories In Linux Make Tech Easier




Chmod Encoding Table Chmod Encoding Table Tek Bahadur Limbu Flickr




Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange
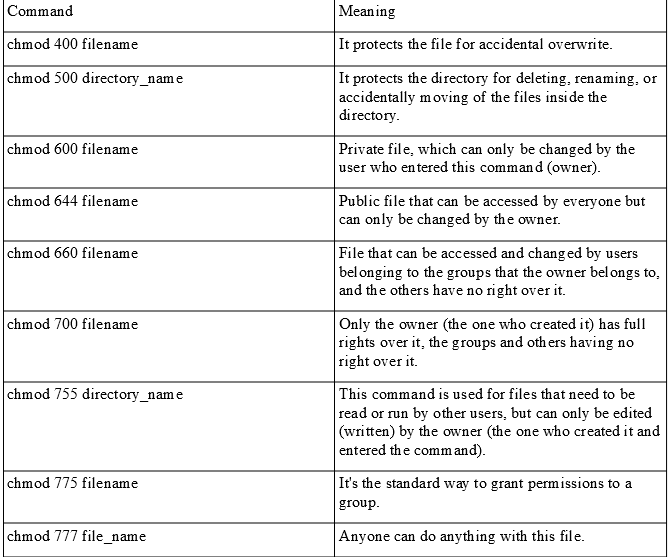



Changing Permissions On A File In Linux Mvps Net Blog




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod Command In Linux Linuxways



Unix Cheat Sheet Open Source Gis Grass Book




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Special Permissions Access Control Filesystem Attributes In Linux Study Com




Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support




How To Modify The Directory Permissions Artbees Wordpress Theme



Understanding File Permissions In Unix Or Linux And Modify Using Chmod



Kitchen Table Talk Chmod Calculator Standaloneinstaller Com




Chmod 755 And Chmod 644 Not Chmod 777 Understanding Wordpress Server File Permissions Youtube




Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets




How Can I Check The Permissions Of A Specific Group Ask Ubuntu




Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach




Tutorial4 Data Representation Numbering Conversion File Permissions Cdot Wiki




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Linux Filesystem Management Ppt Video Online Download




Linux For Beginners Part 6 Understanding File Permission And Ownership Information Technology Blog




Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base



I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs




Chmod Sharing Is Caring




Solved 3 Use Chmod With Octal Number To Forbid All Chegg Com




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
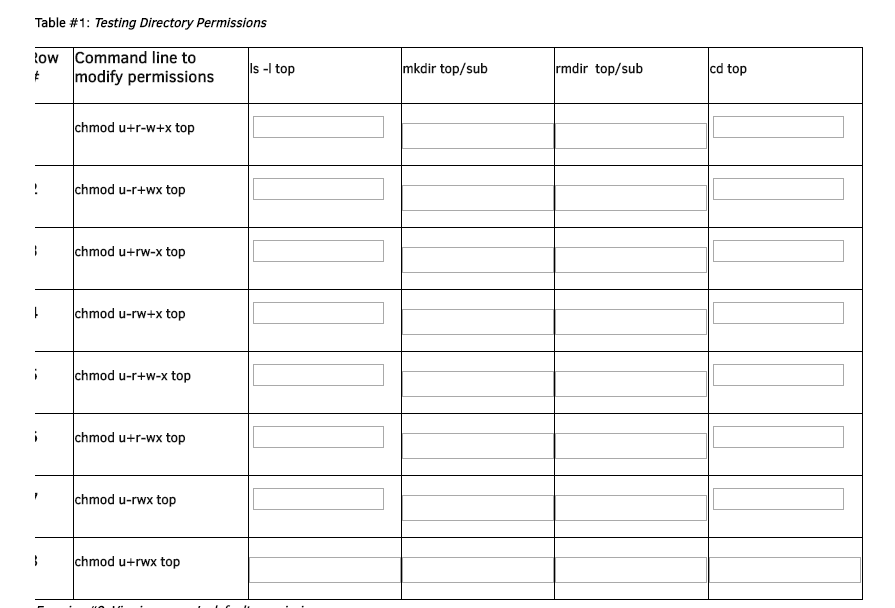



This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Chegg Com




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World



Change File Permissions With Chmod Github




Manage And Fix File Permissions On Android Read Write Execute



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿